In a significant move that signals a new era for the iPhone, Apple is reportedly planning to transition entirely to organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays for all its models by 2025. This decision marks the culmination of a trend that began with the introduction of the iPhone X in 2017, where Apple first adopted OLED technology for its flagship models.
The shift away from liquid crystal displays (LCDs) is a strategic maneuver designed to keep Apple at the forefront of smartphone innovation and ensure its products offer the best possible display quality in an increasingly competitive market.
Table of Contents
The Evolution of Display Technology in Smartphones
To understand the significance of Apple’s decision, it’s important to trace the evolution of display technology in smartphones. The earliest mobile phones featured basic, monochrome screens that displayed only text and simple graphics. As mobile technology advanced, color screens became the norm, and LCDs quickly established themselves as the industry standard. These displays were widely adopted because they were relatively inexpensive to produce and provided decent image quality.
However, as smartphones evolved, so too did the demands placed on their displays. Consumers began to expect more from their devices, particularly as smartphones became central to consuming digital media, gaming, and even professional work. This shift in consumer expectations pushed manufacturers to seek out better display technologies that could offer more vibrant colors, deeper blacks, and improved energy efficiency. OLED technology emerged as the clear answer to these demands.

What is OLED and Why Does It Matter?
OLED stands for organic light-emitting diode, a technology that differs fundamentally from LCDs. While LCDs rely on a backlight to illuminate their pixels, OLEDs generate light individually for each pixel. This difference allows OLEDs to achieve several key advantages over LCDs.
First, OLEDs are capable of producing true blacks. Because each pixel can be turned off completely, an OLED display can achieve a level of contrast that is simply impossible with an LCD. This leads to more vivid and realistic images, which is particularly noticeable when watching high-definition videos or playing graphically intense games.
Second, OLED displays tend to be more energy-efficient, especially when displaying darker content. Since black pixels are effectively off, OLED screens consume less power when displaying images or interfaces with a lot of black or dark areas. This power efficiency can translate to better battery life, a crucial factor for smartphones where battery life is a constant concern.
Third, OLED screens can be made thinner and more flexible than their LCD counterparts. This flexibility opens up new possibilities in terms of smartphone design, allowing for innovations such as curved screens or foldable devices, which have already started to appear on the market.
Apple’s Journey with OLED
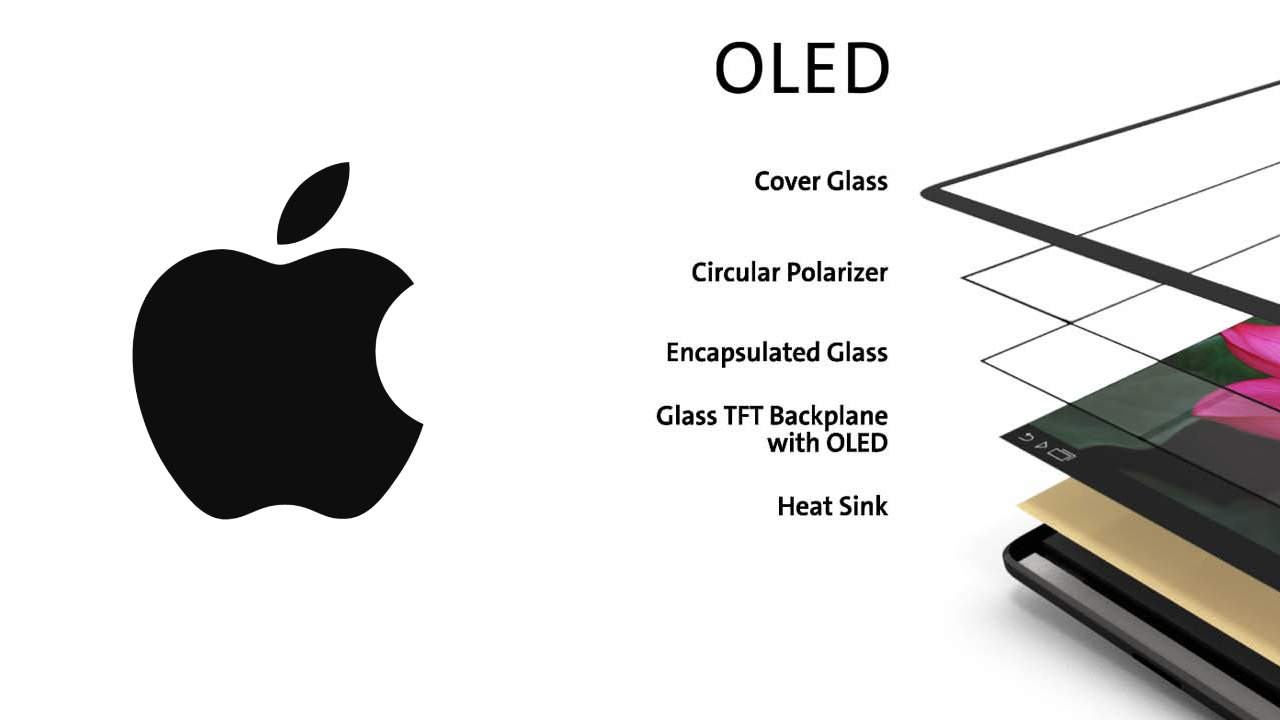
Apple’s relationship with OLED technology began with the iPhone X, the company’s first major redesign of the iPhone since its original launch. The iPhone X was a milestone in many ways, but its adoption of OLED technology was one of the most talked-about features. The OLED display on the iPhone X was a game-changer, offering superior color accuracy, higher contrast ratios, and a more immersive viewing experience compared to the LCD screens used in previous models.
Following the iPhone X, Apple continued to use OLED displays in its premium models, including the iPhone XS, iPhone 11 Pro, and more recently, the iPhone 12 and iPhone 13 series. Each iteration saw improvements in the display’s performance, with Apple refining its technology to offer even better brightness, color fidelity, and energy efficiency.
However, Apple did not immediately abandon LCD technology. For several years, the company continued to use LCDs in its more affordable models, such as the iPhone XR and the iPhone SE. This strategy allowed Apple to offer a range of products that catered to different price points, ensuring that consumers could choose a device that suited their budget without compromising too much on quality.
The Decision to Go All-In on OLED
The decision to switch entirely to OLED displays for all iPhone models starting in 2025 represents a significant strategic shift for Apple. This move suggests that the company believes the benefits of OLED technology are now substantial enough to justify its use across the entire product line, even in more budget-friendly models.
One of the main reasons for this shift is the increasing affordability of OLED technology. When OLED screens first appeared on the market, they were considerably more expensive to produce than LCDs, which is why they were initially reserved for high-end devices. However, as manufacturing processes have improved and production volumes have increased, the cost of OLED displays has come down. This reduction in cost has made it feasible for Apple to consider using OLEDs in all its devices without significantly impacting profit margins or price points.
Moreover, the competition in the smartphone market has become more intense, with rivals like Samsung, Google, and others also adopting OLED technology for their flagship models. By standardizing on OLED, Apple ensures that it remains competitive in terms of display quality, offering consumers the best possible experience regardless of which iPhone model they choose.
The Future of Smartphone Displays
The move to OLED technology across all iPhone models is indicative of a broader trend in the smartphone industry. As consumer expectations continue to rise, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on delivering displays that offer not just better image quality, but also new features and form factors.
One area of particular interest is the development of foldable and flexible displays. OLED technology is inherently more flexible than LCD, making it the ideal choice for devices that need to bend or fold. While foldable smartphones are still in their early stages, they represent a potential future direction for the industry. Apple, known for its cautious approach to adopting new form factors, has not yet released a foldable iPhone, but the switch to OLED could lay the groundwork for such a device in the future.
Another exciting development is the potential for microLED technology, which some experts believe could eventually surpass OLED in terms of performance. MicroLEDs offer many of the same benefits as OLEDs, such as high contrast ratios and energy efficiency, but with the added advantage of being even brighter and more durable. Apple has reportedly been investing in microLED research, and while the technology is not yet ready for mass production, it could play a role in future iPhone models.
